Although late in the EV game, Maruti Suzuki had mega plans for this segment. More than 10,000 crore investment has been earmarked for localization of EVs. The first product will be eVX compact electric SUV, expected to be launched in late 2024. Later in 2026-2027, Maruti will target the entry-level EV space, currently dominated by Tata Tiago EV. In a strategic move, Maruti Suzuki, a key player in the Indian automotive market, has announced plans to launch an entry-level EV to directly challenge competitors, with Tata Tiago EV squarely in its sights. ?
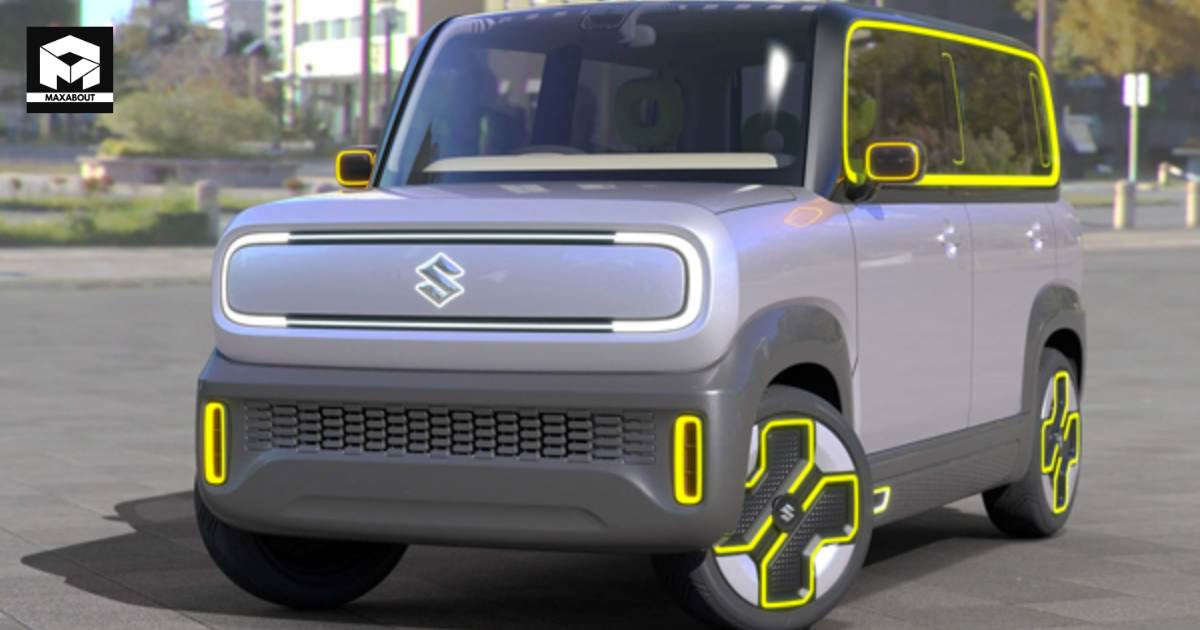
A few years back, Maruti was working on an ICE to EV conversion project in the form of Wagon R EV. That project was scrapped due to cost and technical aspects. Maruti is now developing a born-electric EV architecture (codenamed K-EV) that will be used for its compact electric vehicles. It is different from the eVX that will spawn the Creta EV rivalling compact EV. Similar to the strategy followed by Tata Motors, Maruti Suzuki will also focus on achieving a high level of localization. Suzuki has tie-ups with Denso and Toshiba for manufacturing battery packs. For the upcoming eVX, Suzuki will be sourcing the blade cells from BYD. However, the battery supplier for K-EV small EV could be a different entity.
Key Points
1. Maruti’s Electric Vision: Maruti Suzuki, a brand synonymous with reliability and mass-market appeal, has set its sights on electrification to align with global sustainability goals and India’s push towards cleaner mobility.
2. The Tiago EV Challenge: Tata Motors, with its Tiago EV, has established a foothold in the entry-level electric vehicle segment in India. Maruti’s decision to take on the Tiago EV directly signals its intent to compete in this rapidly growing market. The Tiago EV, known for its affordability and performance, will face formidable competition as Maruti brings its expertise and market understanding to the table.
3. Strategic Timing and Market Trends: Maruti’s decision to launch the entry-level EV in three years is strategic, considering the expected evolution of market trends and infrastructure development.
4. Key Features and Specifications: While specific details about Maruti’s entry-level EV remain undisclosed, industry experts anticipate a focus on range, charging capabilities, and affordability. Maruti’s reputation for understanding the Indian consumer’s needs and preferences will likely manifest in an electric vehicle designed to cater to the mass market, potentially setting new benchmarks in the entry-level EV segment.
5. Charging Infrastructure Development: One of the critical challenges for widespread EV adoption in India is the lack of a robust charging infrastructure.
6. Impact on Competition: Maruti’s entry into the electric segment is expected to shake up the competitive landscape. Established players like Tata Motors will need to innovate and adapt to the evolving market dynamics.
7. Global Perspectives and Collaborations: As Maruti steps into the electric arena, collaborations with global players and leveraging expertise from the parent company, Suzuki, could play a crucial role. Learning from global best practices and incorporating them into the Indian market strategy will be instrumental in ensuring a successful electric vehicle launch.
As the countdown begins for the launch in three years, the industry and consumers alike will keenly observe how Maruti positions itself against the competition, addresses challenges, and contributes to the larger goal of sustainable and electrified mobility in India. As of now, electric vehicles are sold at a premium. In the case of ICE Tiago and its EV version, the price difference is around 35%. Such price gaps are expected to reduce in future, as production volumes increase and battery prices fall. It will allow a faster transition from ICE to EVs. It will still be a long journey, as EV share in overall PV sales in 2023 was just around 2 percent.
2024-01-12 18:01:03
